
Medical Weight Loss Explained
A lot is said about medical weight loss but we are here to debunk the myths for you.
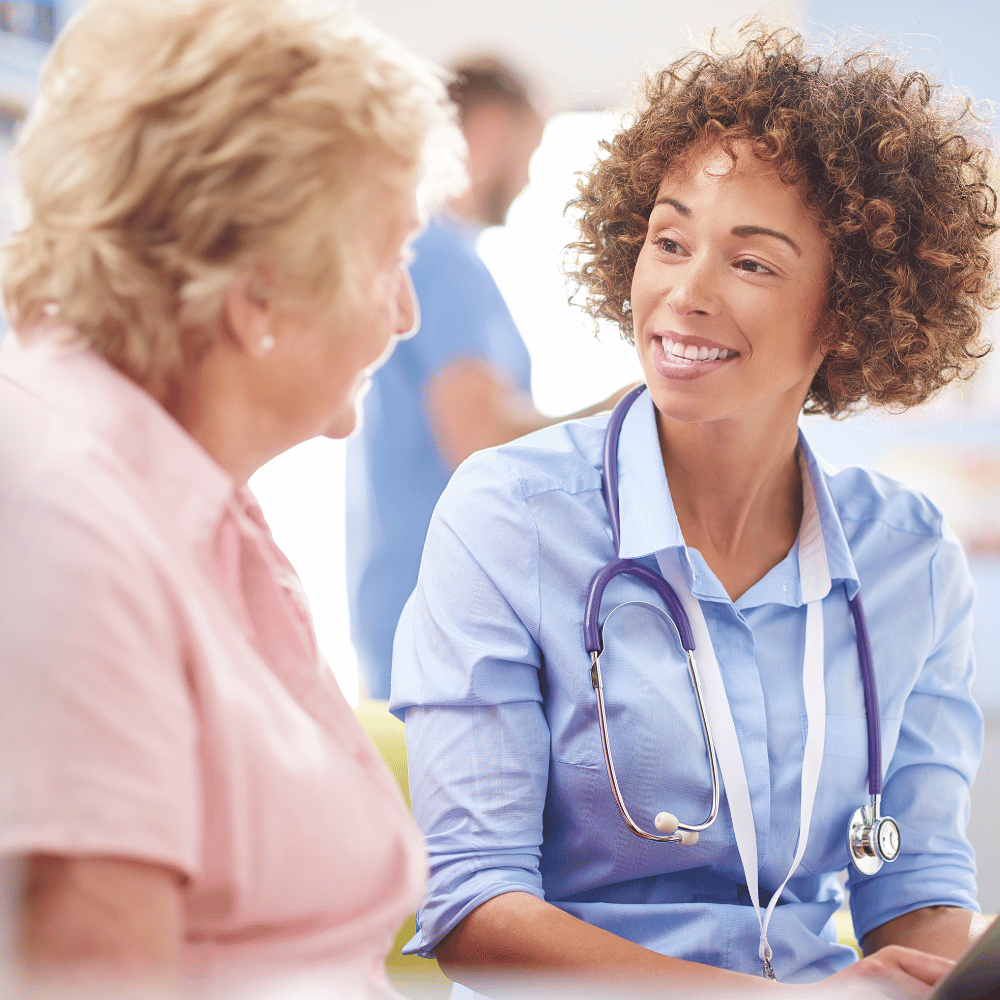
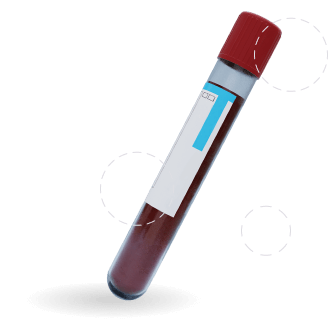
Blood Tests > Diabetes Testing

Find Out More


By the end of 2010, 2.8 million people were diagnosed with diabetes in the UK, and by 2021 more than 4.4 million people in the UK live with diabetes.
Plus, 1.2 million people could be living with type 2 diabetes who are yet to be diagnosed.
Therefore, it is safe to say, diabetes is one of the most prevalent diseases in the UK, and when left untreated it can cause serious long-term complications.

*Please note that HbA1C results continue to be delayed nationwide and turnaround time is currently 3 days. This is part of our platinum profile and diabetes screen. Update: 11.11.2024*
The two most common types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 is an autoimmune, genetic disorder where your immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas. This type of diabetes typically develops in children, teenagers, and young adults, but it can occur at any age.
Type 2 (also known as adult-onset diabetes) occurs when your body stops using insulin properly, and over time, it leads to elevated blood glucose levels. Type 2 diabetes is a preventable disease.
Both types of diabetes affect how your body uses sugar (glucose) for energy, and symptoms include thirst, urination, and weight loss.
An HbA1c test is the main blood test used to diagnose diabetes. HbA1c stands for glycated hemoglobin (or hemoglobin A1c). Hemoglobin is the protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen through your body. HbA1c measures the amount of sugar attached to your hemoglobin( blood sugar levels) for the last two to three months.
Your typical HbA1c blood test results should show an HbA1c value below 5.7 %. Anyone with an HbA1c value between 5.7 % to 6.4 % is considered to be prediabetic, and diabetic with a HbA1c value of 6.5% or higher.


Symptoms include urinating often, feeling very thirsty all the time, being very hungry (even when you are eating), extreme fatigue, blurry vision, cuts and bruises that are slow to heal, frequent infections, and areas of darkened skin (usually on your arms and neck).
Additional symptoms include unintended weight loss (type 1) and tingling, pain, or numbness in your hands and feet (type 2).
If you suspect you are a diabetic, we implore you to get a diabetes blood test done.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas. However, factors that could increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes include:
Use our online booking engine or book your test by giving us a call.
On the online booking engine select the “appointment type” you need.
You will be seen by one of our friendly phlebotomists or trained clinicians.

Your doctor will thoroughly explain all the steps you need to take before your diabetes blood test. Fasting for 8 to 12 hours before the test is typical. Remember to inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as certain medications can affect your blood glucose levels.

Diabetes screening involves a straightforward blood test where a needle is typically inserted into a vein, usually located near the inner arm. A small amount of blood is then drawn for analysis. During this process, you may experience a slight stinging sensation at the site of the needle insertion, but it will quickly subside.

The test price covers the cost of collecting your blood sample and delivering the results to you via email. If you wish to have one of our doctors interpret your results, a consultation fee will apply. We highly recommend scheduling a consultation before undergoing any testing, as this will enable you to discuss the most suitable options for your needs.
No
Hidden Charges
Transparent fees. The price you see is the price you pay.
No GP consultation
needed
No GP appointment requirement for blood tests
Established
since 1998
Experienced doctors & a professional team.
Strictly
confidential
Your medical records are kept private at all times.
We offer a wide range of private blood tests in London. Same-day appointments are available 5 days a week.
We work with experienced consultants & healthcare professionals who have received positive feedback from our patients, and with whom we have established long-term relationships.
Latest Episode
Tune in to our podcast to explore the world of healthcare and learn from distinguished special guests. We cover everything from preventative measures to cutting-edge treatments so that you can stay informed and up-to-date on health-related things.

A lot is said about medical weight loss but we are here to debunk the myths for you.

Tourist in London and need a GP? Get fast, private care for illnesses, injuries, or lost medication. No registration needed.

With NHS appointments harder to access, many people are turning to private GPs for faster, more convenient care.
Subscribe for latest updates & news


From same-day private GP and blood test appointments to visa medicals, a sexual and reproductive health clinic, and preventative health screenings, we are here to help.
Contact Us
Accepted Insurance Companies






Please note that Walk-in Clinic is a private medical centre & not an NHS service. Harley Walk-in Clinic Ltd company registration no. 07472804